“Let us, on this International Day, reaffirm our commitment to translating solidarity into positive action. The international community must help steer the situation towards a historic peace agreement.” That is UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon’s message for the International Day of Solidarity with the Palestinian People, 29 November 2011.
Mr. Ban called on the Israeli and Palestinian leadership to show courage and determination to seek an agreement for a two-State solution that can open up a brighter future for Palestinian and Israeli children.
There have been many Middle East peace proposals and many negotiations including an Arab state, with or without a significant Jewish population, a Jewish state, with or without a significant Arab population, a single bi-national state, with or without some degree of cantonization, two states, one bi-national and one Arab, with or without some form of federation, and two states, one Jewish and one Arab, with or without some form of federation.
During the 19th Century some Jews banded together to form a political ideology called Zionism, based on the idea of a “Jewish homeland.” In the USA the Zionist movement developed a powerful political lobby to promote its aims, while its military groups pursued a violent terrorist campaign in Palestine against the Arabs and Britain to force acceptance of its demands.
On 29 November 1947 the United Nations adopted a partition resolution dividing the land of Palestine into two independent states- one Arab and one Jewish, while Jerusalem was put under international protection. This was accepted by most of the Jewish settlers, who comprised 13% of the population and rejected by the majority Arab population, the original inhabitants who demanded self–determination. The British said the decision would be a failure and refused to apply it. When British forces withdrew in May 1948, and Israel declared independence fighting broke out between Arabs and Jews.
One of the first plans for settling the Arab-Israel war of 1948 was made by the UN emissary, Count Folke Bernadotte. Count Folke Bernadotte was a Swedish noble and diplomat, nephew of the Swedish king, fluent in six languages; he was an outstanding humanitarian and very well respected for his integrity. He gained international recognition through his work as head of the Swedish Red Cross during World War Two, organizing exchanges of disabled prisoners. Bernadotte also used his position to negotiate with Heinrich Himmler, a military commander, and a leading member of the Nazi Party, and save the lives of about 30,000 Jews, Allied prisoners of war and other people from the concentration camps, just before the end of the war.
On 20th May, 1948, the United Nations Security Council appointed Bernadotte as mediator in the Arab-Jewish conflict in Palestine. After meeting Arab and Jewish leaders he succeeded in obtaining a 30-day truce that began on 11th June. In then developed his first plan for peace.
First Proposal
Bernadotte’s first plan called for the Jewish State to relinquish the Negev and Jerusalem to Transjordan and to receive the western Galilee. Bernadotte advocated a total demilitarization of Jerusalem and blamed the Jewish forces for “aggressive” behavior in the city.
The Arab world rejected the Bernadotte plan on the grounds that, as Syrian officer Muhammad Nimr al-Khatib said, “Most of these mediators are spies for the Jews anyway.” The Israeli government, hating the idea of giving up Jerusalem and bent on military victory, quickly followed suit. Fighting resumed on July 8 and the Israeli army gained strength and succeeded in pushing back the Arabs until a second UN cease-fire was declared on July 18, this time with no time limit and a threat of economic sanctions against any country that broke it.
After the unsuccessful first proposal, Bernadotte continued with a more complex proposal that abandoned the idea of a Union and proposed two independent states. Having witnessed the expulsion of the Palestinians from their home, he called for the unqualified return of all Palestinian refugees expelled as a result of the conflict. He declared:
“The right of innocent people, uprooted from their homes by the present terror and ravages of war, to return to their homes, should be affirmed and made effective, with assurance of adequate compensation for the property of those who may choose not to return…. [N]o settlement can be just and complete if recognition is not accorded to the right of the Arab refugee to return to the home from which he has been dislodged. It will be an offence against the principles of elemental justice if these innocent victims of the conflict were denied the right of return to their homes while Jewish immigrants flow into Palestine…”
Second Proposal
This proposal was completed on September 16, 1948 and it contained what he described as “seven basic premises” regarding the situation in Palestine:
- Peace must return to Palestine and every feasible measure should be taken to ensure that hostilities will not be resumed and that harmonious relations between Arab and Jew will ultimately be restored.
- A Jewish State called Israel exists in Palestine and there are no sound reasons for assuming that it will not continue to do so.
- The boundaries of this new State must finally be fixed either by formal agreement between the parties concerned or failing that, by the United Nations.
- Adherence to the principle of geographical homogeneity and integration, which should be the major objective of the boundary arrangements, should apply equally to Arab and Jewish territories, whose frontiers should not therefore, be rigidly controlled by the territorial arrangements envisaged in the resolution of 29 November.
- The right of innocent people, uprooted from their homes by the present terror and ravages of war, to return to their homes, should be affirmed and made effective, with assurance of adequate compensation for the property of those who may choose not to return.
- The City of Jerusalem, because of its religious and international significance and the complexity of interests involved, should be accorded special and separate treatment.
- International responsibility should be expressed where desirable and necessary in the form of international guarantees, as a means of allaying existing fears, and particularly with regard to boundaries and human rights.
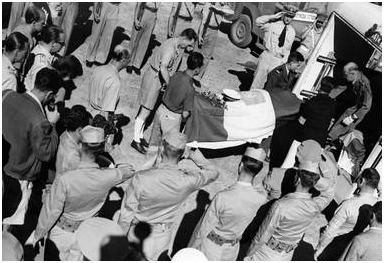
On 17 September 1948, the day after he submitted his progress report to the UN, a four-man team of the Jewish nationalist Zionist group Lehi (commonly known as the Stern Gang or Stern Group) ambushed Bernadotte’s motorcade in Jerusalem’s Katamon neighborhood.
The four hit men were, in fact, Stern Gang members consisting of three gunmen and a driver. The three gunmen were Yitzhak Ben-Moshe, “Gingi” Zinger, and Yehoshua Cohen. Cohen was the shooter who murdered Bernadotte. The fourth member of the hit team, the jeep driver, was Meshulam Makover.
Of the three Stern Gang leaders who dispatched the killers, Israel Eldad, Natan Yalin-Mor and Yitzhak Shamir, only Yalon-Mor was brought to trial along with one gang member, Mattiyahu Shmulovitz. They were not charged with Bernadotte’s murder but with membership in a terrorist organization. Following their conviction Yalon-Mor and Shmulovitz were pardoned under a general amnesty ordered by Ben-Gurion after serving only two weeks in jail.
Based upon events in Israel following Bernadotte’s assassination it is apparent that being a member of the Stern Gang was not blight on one’s good name but a career-enhancing credential. For example, Natan Yalin-Mor was elected to a seat in the First Knesset, the Israeli parliament. The shooter, Yehoshua Cohen, became Ben-Gurion’s personal bodyguard. In 1983, Yitzhak Shamir succeeded Menachem Begin as Prime Minister.
From 1948 through to the present day, the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians is ongoing. After all these years, the only unanswerable question is the one that was asked by Bertrand Russell in his message to the International Conference of Parliamentarians held in February 1970:
The tragedy of the people of Palestine is that their country was ‘given’ by a foreign power to another people for the creation of a new state. The result was that many hundreds of thousands of innocent people were made permanently homeless. With every new conflict their numbers increased.
How much longer is the world willing to endure this spectacle of wanton cruelty?
It is abundantly clear that the refugees have every right to the homeland from which they were driven, and the denial of this right is at the heart of the continuing conflict.
Sources:
http://www.1948.org.uk/right-of-return/
http://www.timeanddate.com/holidays/un/solidarity-day-palestinian-people
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proposals_for_a_Palestinian_state
http://www.zionism-israel.com/dic/Bernadotte_Plan.htm
http://www.spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk/COLDbernadotte.htm
http://usa.mediamonitors.net/content/view/full/49384
http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/History/folke.html
http://suspiciousdeaths.blogspot.com/2010/06/count-folke-bernadotte.html


 sending...
sending...
